Gutenberg WordPress Block-Based Editor The Definitive Guide
I am sure that you have noticed a lot of things going on recently in the WordPress community!
Well, it is regarding WordPress 5.0 release along with the new block-based content editor, Gutenberg.
WordPress 5.0 has introduced some big upgrades this year. In addition to it, Gutenberg is considered as the first step towards the future!
But before we move ahead and dive into the deep knowledge about Gutenberg WordPress Editor.
I would recommend you to have a quick read on our detailed article - What’s new in WordPress 5.0?
Now that you have already know about WordPress 5.0 and things to expect from the Block-Based Editor.
It’s time to explore Gutenberg, it features, working, it’s future, pros, and cons one by one.
Diving Into the New WordPress Gutenberg Editor
Chapter 1 Gutenberg Introduction The New Gutenberg Editing Experience
What is Gutenberg?
Gutenberg editor is introduced with the release of WordPress 5.0. The name was kept after Johannes Gutenberg.
Is the new generation block-based content editor with streamlined editing experience.
It is now more easy to create any complex layout without having any coding experience or WordPress builder.
Goal of Gutenberg Editor
The main goal of the Gutenberg editor is to make the building process of a WordPress blog or website – More Easy and Approachable to Non-coders.
Here’s what Matt Mullenweg said about Gutenberg –

“The editor will endeavor to create a new page and post building experience that makes writing rich posts effortless, and has “blocks” to make it easy what today might take shortcodes, custom HTML, or “mystery meat” embed discovery.”.
Bye bye TinyMCE editor (Classic Editor)
Gutenberg is the replacement of WordPress TinyMCE editor which was based on the WYSIWYG text editor.
Though WordPress has replaced classic editor with Gutenberg but it is still available as a WordPress plugin and will be maintained until at least 2022.
Transformation of WordPress Editor From Classic to Gutenberg Block-Based
Transformation of WordPress editor from classic to Gutenberg block-based editor has brought a complete change in the editing experience.
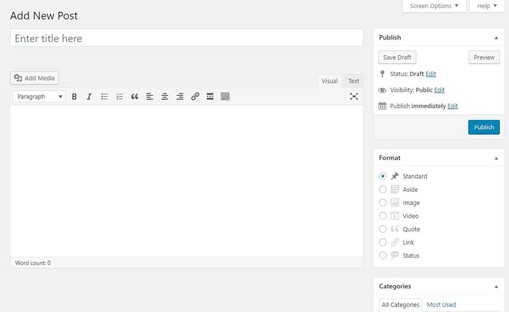
Classic TinyMCE WordPress Editor
Block-based Gutenberg WordPress Editor
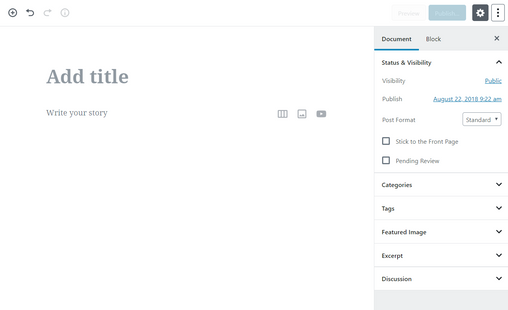
In the classic editor,
- you need to add images, galleries, shortcodes, video embeds via iframes and other content elements in the same text window.
Unlike the classic editor, Gutenberg is composed of blocks.
- It has completely changed the editing experience by bringing in the block-based approach to the content.
In simple words, Gutenberg has replaced the single edit field of the classic WordPress TinyMCE editor with lots of individual “blocks”.
Chapter 2 Advanced Gutenberg Blocks A Complete List on How to Use Them
I’ve used the term “block” a couple of times in the above content but yet not explained it!
So, let’s take a look at what a Gutenberg block exactly is and types of blocks that comes with Gutenberg.
What is Gutenberg Block?
A Gutenberg block is nothing but a wrapper or an abstract unit to compose and organize the content element.
For Example: paragraph, quote, image, video etc.
Blocks are hierarchical in nature and one block can be a child or parent, static or dynamic.
Unlike the classic editor,
- Each block has its own toolbar, attributes or configuration settings.
- Gutenberg has added blocks for widgets, shortcodes, and embeds.
What Types of Blocks are Included in the Gutenberg?
Gutenberg blocks are divided into 6 different types or categories –
1 Inline Elements (1 Block)
Right now there is only one block in the inline elements category. I will add more information based on the upcoming updates.
- Inline Image
2 Common Blocks (10 Blocks)
Gutenberg has provided a total of 10 commonly used blocks for a post or a page.
Below is the list of those elements.
- Paragraph
- Image
- Heading
- Gallery
- List
- Quote
- Audio
- Cover
- File
- Video
3 Formatting Blocks
There are a total of 7 blocks for formatting which includes code, preformatted, custom HTML and table. There were no options before to add a table in the classic editor other than a plugin or to hardcode in the text window of the classic editor.
But now there’s a block to do so.
- Code
- Classic
- Custom HTML
- Preformatted
- Pullquote
- Table
- Verse (for poetry)
4 Layout Elements (7 Blocks)
Gutenberg has brought some awesome layout options to a post such as columns, side-by-side text, separator etc.
There are a total of 7 blocks in this category. It certainly has increased the flexibility in terms of layout and structure.
- Columns
- More
- Page Break
- Separator
- Spacer
- Media
- Text – side-by-side
5 Widget Blocks (5 Blocks)
There was no option to use widgets in a post in the classic editor, but now it’s possible to display widgets inside a WordPress post.
For now, there are only 4 widgets that can be added to a WordPress post.
Apart from the 4 widgets, there’s also a block available to add shortcode in the widget category.
- Shortcode
- Archives
- Categories
- Latest Comments
- Latest Posts
6 Embed Blocks (34 Blocks)
WordPress always asked not to use iframes in the post. Now it’s easy to embed YouTube videos, Facebook posts, Twitter posts, Instagram posts, and much more.
Gutenberg has introduced a total of 34 embed blocks in its initial version.
Below is the complete list of embed blocks.
- YouTube
- Vimeo
- Imgur
- Tumblr
- SoundCloud
- Flickr
- Spotify
- Animoto
- Cloudup
- CollegeHumor
- Dailymotion
- Funny or Die
- Hulu
- Issuu
- Kickstarter
- Meetup[dot]com
- Mixcloud
- Photobucket
- Polldaddy
- ReverbNation
- Screencast
- Scribs
- Slideshare
- SmugMug
- Speaker Deck
- TED
- VideoPress
- WordPress.TV
- WordPress[dot]com
The above blocks are limited in numbers right now, but more default blocks will get added from the WordPress community in the upcoming updates.
Reusable blocks
Apart from the default blocks, there is another block category which comes empty by default – Reusable Blocks.
You can now save your often used content element or same styled content as a reusable block for later use.
For Example: I’ve added some shortcodes I often use in my posts. Every time either I had to copy it from a previous post or write it manually, but now I don’t even have to remind it.
I’ve saved it as a reusable block and named it. All I’ve to do is to select the block and done.
Additional Plugin Blocks
You might see some additional Gutenberg blocks other than the default ones. Consider that those extra blocks are coming from the plugins installed on your website.
For example – Yoast SEO plugin adds 2 Yoast Structured Data Gutenberg blocks – How-to Block and FAQ Block.
Blocks For Developers
If you’re a developer, then you can create your own blocks by using Block API by WordPress.
Now that Gutenberg is officially a part of WordPress 5.0, we will see even more blocks by both WordPress & third-party developers.
Chapter 3 Gutenberg WordPress Editing Interface Elements
After reading this section, you will completely understand the –
- WordPress 5.0
- Gutenberg Editor User Interface
Gutenberg editor for WordPress users is divided into 3 parts –
- Top Menu Bar
- Sidebar
- Content/Block Area
Top Bar Menu
The top menu bar is the first thing you will notice as it is located at the top of the screen displaying 10 options as shown in the image given below –

Let’s know more about each options of the Top Menu bar –
1 Add New Block
The Add Block option opens up the list of Gutenberg’s Blocks and embeds you can add to your post and page. You can use the search bar or scroll through the options to find the desired block you want to add.
The Gutenberg Editor’s “Most Used” Block options by default include: paragraph, heading, list, gallery, image, quote, spacer, video, and cover block.
2 Undo & Redo Buttons
Undo button – Undo the last change you made.
Redo button – Redo your last undo.
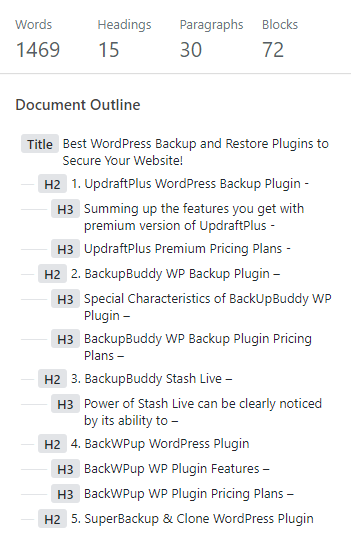
3 Content Structure
This button gives a quick overview of the content in a WordPress post or page, which includes the word count, the number of headings, paragraphs and the number of blocks that you have used.
It also displays the Document outline, with which you can make sure if your WordPress post or page is following a proper heading hierarchy or not.
Heading hierarchy plays an important role in SEO and Google Rankings.
So, content structure is similar to the document outline displayed on the left of the Google Docs document.
4 Block Navigation
Block Navigation keeps track of all the blocks used and maintain the same order they are used.
For example – You added a heading block followed by 2 paragraph blocks followed by a separator, then block navigation will display something like this –
- Heading, Paragraph, Paragraph, Separator, And so on.
You can also jump between the Gutenberg Blocks in your WordPress post or page just by clicking on any block displayed in the block navigation.
5 Save Draft, Preview & Publish Buttons
Save Draft – Save Draft button lets you save your WordPress post or page as a draft. Though Gutenberg autosaves the post or page, you still can save it manually by clicking on the save draft button.
Preview – The Preview button opens up a front-end version of the post or page in the new tab. You can check how your post or page is looking at the front end.
Publish – Publish button makes your WordPress post or page live and available to the public.
6 Settings
The Settings button toggles the right sidebar settings menu on and off.
7 More Options
The last button with the three vertical dots displays the following settings –
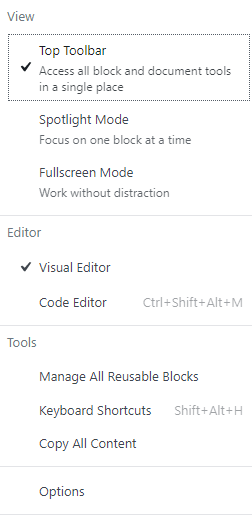
1. View
View includes the Top Toolbar, Spotlight Mode, Full-Screen mode.
- The Top Toolbar Mode adds the editing options of a block to the top toolbar.
- Spotlight Mode allows you to focus on one block at a time to avoid distractions.
- Full-Screen Mode also allows you to work without distraction by removing left dashboard menu items and sidebar options.
2. Editor
Switching between Visual Editor and Code Editor can be helpful for developers or advanced users. Code Editor displays the code generated by the block.
3. Tools
This section contains the following options
- Manage All Reusable Blocks
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Copy All Content
Sidebar Settings
Gutenberg editor’s sidebar is divided into 2 sections –
- Document Settings
- Block Settings
1 Document Settings
Document Settings are pretty much similar to classic editor’s sidebar. Below is the list of settings that resides in the document tab of the components panel –
- Status & Visibility
- Revisions
- Permalink
- Categories
- Tags
- Featured Image
- Excerpt
- Discussion
- Post/Page Attributes
2 Block Settings
When a block is selected, the block settings gets enabled for that particular block. Block settings vary according to the block type. Some blocks may have formatting settings while other might have customization settings.
For Example – Color and font settings appear when a paragraph block is selected but latest post settings when Latest Post Widget block is selected.
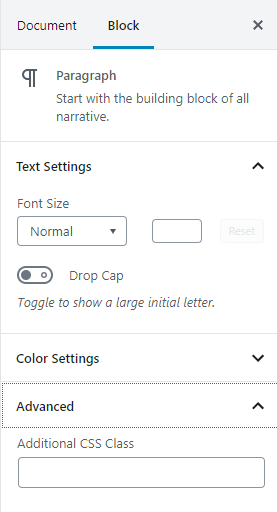
The Advanced Setting Block –
The Advanced setting is present in each block settings and lets you add CSS class to the selected block. By adding CSS class, you can add additional styles to the Block.
Content / Block Area
This is the area where all the blocks and your post’s content gets displayed. It is similar to the classic editor’s text area.
The sections and settings that gets displayed in the content/block area includes –
1 Post Title
Here you can add title or heading of your article.
2 Individual/Inline Block Settings
These settings get enabled when you click a block to edit.
3 Change Block Type
Each Block has an option to change the block type. A block can only be changed to one of the pre-selected blocks provided to you.
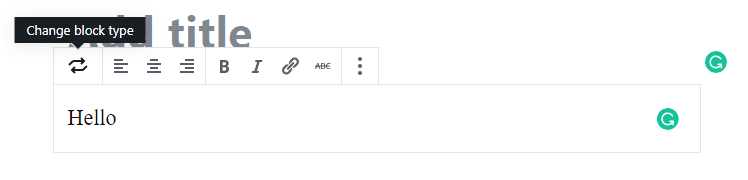
4 Edit Block
Edit options will be displayed depending on the selected block type.
For example, in the above image formatting options gets displayed because it’s a paragraph block.
5 More Gutenberg Options
Each block has additional settings which get displayed when the vertical 3 dot icon on the right-most gets clicked.
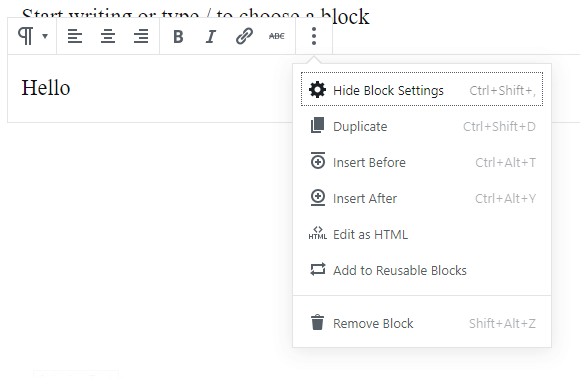
Hide & Show Block Settings – This button toggles the right sidebar block settings menu on and off.
Duplicate – This option duplicates the selected block.
Insert Before – This option lets you insert a new block before the selected block.
Insert After – This option lets you insert a new block after the selected block.
Edit as HTML – This option lets you edit the block as HTML. By switching to HTML mode, you can add styles, CSS classes to the block.
Add To Reusable Blocks – This option lets you save the selected block for later use.
Remove Block – You can remove the selected block anytime by clicking on ‘Remove Block’.
Chapter 4 How the WordPress Gutenberg Editor Works?
Now that you are well aware of the Gutenberg, blocks, block types and editor’s new interface and terminology.
In this section, you will know – How Gutenberg block-based WordPress editor works? It’s pros and cons, plus What to expect in the future.
Those blog post or articles which says you to install the Gutenberg WordPress plugin from the WordPress.org Directory are outdated. As, installing the Gutenberg plugin was required in beta version.
Let’s move on to the working of the Gutenberg editor dashboard.
How To Add A Block?
Step #1 – You can easily add a block in the Gutenberg editor
- By clicking on the plus button (+) visible in the top bar
- Or by clicking on the plus button (+) appearing in the block/content area just below the post title.
Step #2 – When you click on the plus icon, a dropdown will get open with the list of blocks.
Step #1 – You can select the desired block from the list and block will be added to the content area.
How To Edit A Block?
Step #1 – To edit any block, you just need to select the block you want to edit the content of.
Step #2 – When you click on the block to edit –
- Inline-block settings get enabled where you can edit its formatting, add the block as a reusable block, edit the block as HTML or remove the block.
- Block settings get enabled on the sidebar from which you add additional CSS class, change the styling or customize settings depending on the block type you selected.
How To Change Block Settings?
When you select a block, its settings gets displayed on the right panel under the block tab. You can make changes from there.
For example – Below are the settings of the paragraph block which includes font size, background color, text color etc.
How To Search A Block In Gutenberg?
You can even search the block by its name.
For Example – If you want to add a paragraph block, then you can search the paragraph in the dropdown list and select it directly from the search results.
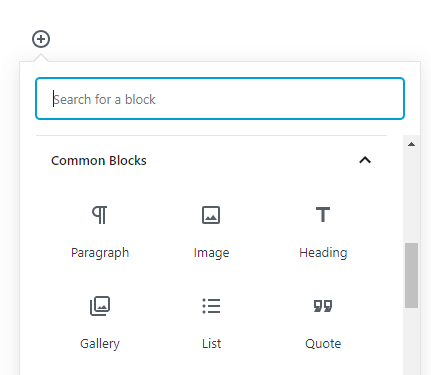
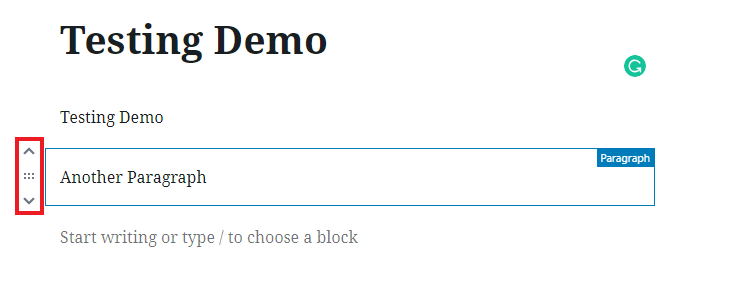
How To Rearrange Individual Gutenberg Blocks?
Every block has 3 options on the left of the selected block with which you can re-adjust the position of the block.
- Up arrow – It moves the block above of its previous block.
- Down arrow – It moves the block after its next block.
- Drag Icon – You can drag the block to up and down with this drag option.
How To Edit Existing Content In The Gutenberg Editor?
There are 2 ways to edit the existing content in the Gutenberg Editor –
METHOD #1 – Edit The Content Without Converting It To Blocks – Either you can edit the existing content inside the ‘Classic Block’ without converting it to blocks.
METHOD #2 – Convert The Existing Content To Gutenberg Blocks – We’ve covered the process in our next section.
How To Convert Existing Content To Gutenberg Blocks?
You can easily convert the existing content to the Gutenberg blocks by following the steps mentioned below –
Step #1 – Select the ‘Classic Block’ which you want to convert to Gutenberg blocks.
Step #2 – The moment you click on the ‘Classic Block’, editing settings will appear instantly and you need to click on the 3-dot icon placed at the last.
Step #3 – You need to click on ‘Convert To Blocks’ from the drop-down.
Step #4 – Convert To Blocks automatically converts your Classic Editor’s existing content to Gutenberg blocks.
Chapter 5 Pros and Cons of the new Gutenberg WordPress Editor
Everything comes with pros & cons, so does Gutenberg WordPress editor.
And it’s important to understand the positives and negatives if you’re going to deal with the new WordPress Gutenberg editor, isn’t it?
So let’s check the positives and negatives of using Gutenberg WordPress editor.
Gutenberg Pros
PRO #1 – No need to have technical or coding knowledge or even hire a developer.
Make a custom and complex layout for a page or post all by yourself with ease.
PRO #2 – WordPress community is aiming it to make it more intuitive and flexible like –
Medium, Wix, and Squarespace for new users.
PRO #3 – Gutenberg has certainly increased user-friendliness and improved editing experience when compared to the classic WordPress editor.
PRO #4 – Now it’s possible to create an advanced design without relying much on TinyMCE.
PRO #5 – WordPress community has taken countermeasures of Google’s Mobile First Index announcement by creating the Gutenberg which works very well on mobile and certainly has increased the mobile responsiveness in comparison to the classic editor.
PRO #6 – Gutenberg has certainly increased the screen space and lessened the distractions present in the classic editor.
More screen space provides a great user experience while writing content or creating layouts.
PRO #7 – Gutenberg's Full-screen mode experience is awesome! First, I use to write my blog posts on Google docs as it was comfortable and less distracting.
But Gutenberg has exactly provided me the same experience when switched to full-screen mode.
PRO #8 – Nothing has changed for hardcore developers as they can still create customized blocks using HTML.
So it’s a decent Christmas gift by WordPress for both technical and non-technical users.
PRO #9 – Gutenberg stores meta information about the blocks in HTML comments.
This is very useful for developers and advanced users as it can only be seen on the back-end and have no effect on the front-end.
PRO #10 – In the classic editor, when a user copies a piece of content from a different location say Google docs, one has to manually clear the formatting first to assign the style according to their needs.
But the new block-based Gutenberg editor has certainly improved the copy-paste experience as neither the formatting gets lost nor it made a mess.
PRO #11 – Gutenberg automatically detects the type of content you’re pasting and create a block accordingly.
For example, if you will paste an ordered list, Gutenberg automatically creates a list block and paste the content in the clipboard.
Gutenberg Cons
CON #1 All the third-party themes and plugins are still not compatible with the Gutenberg editor. Especially that require integration with TinyMCE.
It might take some time for theme and plugin owners to provide a stable version of their product.
CON #2 – Backward compatibility has been provided for meta boxes in both the native and custom post types.
Still, it’s a long road to make everything compatible with Gutenberg.
CON #3 – It’s true that the goal of Gutenberg is to make editing experience more intuitive but many users are finding Gutenberg a bit complicated and complex.
CON #4 – User ratings on WordPress page of Gutenberg plugin page are very low when it was launched as a plugin.
That’s because there were many bugs and it was at its initial stage.
CON #5 – People are still finding a lot of issues and bugs in the editor, and WordPress community is working pretty hard to resolve them and make Gutenberg more user intuitive.
Gutenberg WordPress Editor is the Future

Gutenberg is definitely like a revolution in the WordPress community. It is the first step towards the future.
It’s a blessing for non-developer users as they can design even a complex layout easily using Gutenberg. It is all possible because of the advanced blocks that have been introduced like columns, buttons, advanced settings etc.
After you spend some time with Gutenberg new content WordPress editor, I am sure you are going to like it! smile
Now I would like to hear from you which editor would you prefer? Old Classic editor or the all New Gutenberg WordPress editor!
Have you started working on the new editor? Then, share your thoughts in the comments below!


